NEWYou can now listen to Fox News articles!
NASA’s Curiosity rover is getting a firsthand look at a region on Mars previously only seen from orbit that features a “boxwork” pattern, along with evidence of ancient waterways, including rivers, lakes and maybe an ocean.
New images and data from the Mars rover have already raised questions about how the red planet’s surface was changing billions of years ago. Scientists are still unable, though, to answer why the planet’s water eventually dried up and converted the surface into a chilly desert.
Curiosity rover is in an area called Gale Crater, and evidence has shown that when it was formed, water was percolating under the surface.
NASA said the rover had found evidence of groundwater in the crater when it encountered crisscrossing low ridges, some of which were only a few inches tall and were described by geologists as being arranged in a boxwork pattern.
ARCHAEOLOGISTS EXCAVATE ANCIENT WORKSHOP WITH UNFINISHED SCULPTURES ON GREEK ISLAND
Beneath the ridges is bedrock scientists believe formed when groundwater trickled through the rock and left behind minerals that accumulated in the cracks and fissures. The minerals then hardened and became cement-like.
The formations were worn away after what NASA called “eons of sandblasting” from Martian wind, though the minerals remained and revealed a network of resistant ridges within.
Rover has already analyzed ridges that scientists say look more like a crumbling curb.
HISTORY BUFF UNCOVERS LOST MEDIEVAL MONASTERY THANKS TO STRANGE MAP SYMBOL
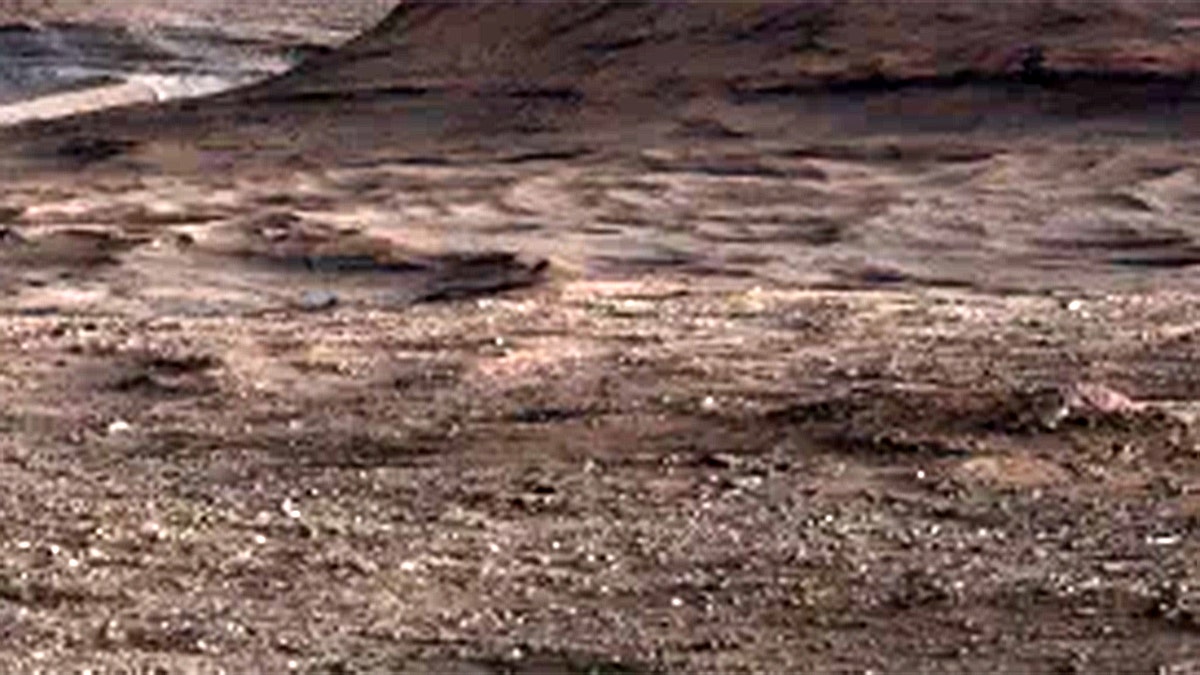

But the patterns created over time stretch across miles of a layer on the 3-mile-tall Mount Sharp. The rover has been climbing the foothills of Mount Sharp since 2014, NASA said.
What scientists also find interesting about the boxwork patterns is they have not been found anywhere else on the mountain by orbiters overhead or Curiosity.
“A big mystery is why the ridges were hardened into these big patterns and why only here,” said Curiosity project scientist Ashwin Vasavada of NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California. “As we drive on, we’ll be studying the ridges and mineral cements to make sure our idea of how they formed is on target.”
NASA said the patterns are found in a part of Mount Sharp formed during various eras of the ancient Martian climate. So, as the rover ascends from the oldest layers to the youngest, it is essentially time traveling and searching for signs that water existed on Mars and which environments would have supported microbial life in the planet’s ancient times.
ANCIENT BEDROCK KITCHENS REVEAL EVIDENCE OF HISTORICAL FOOD PRACTICES, EXPERTS SAY
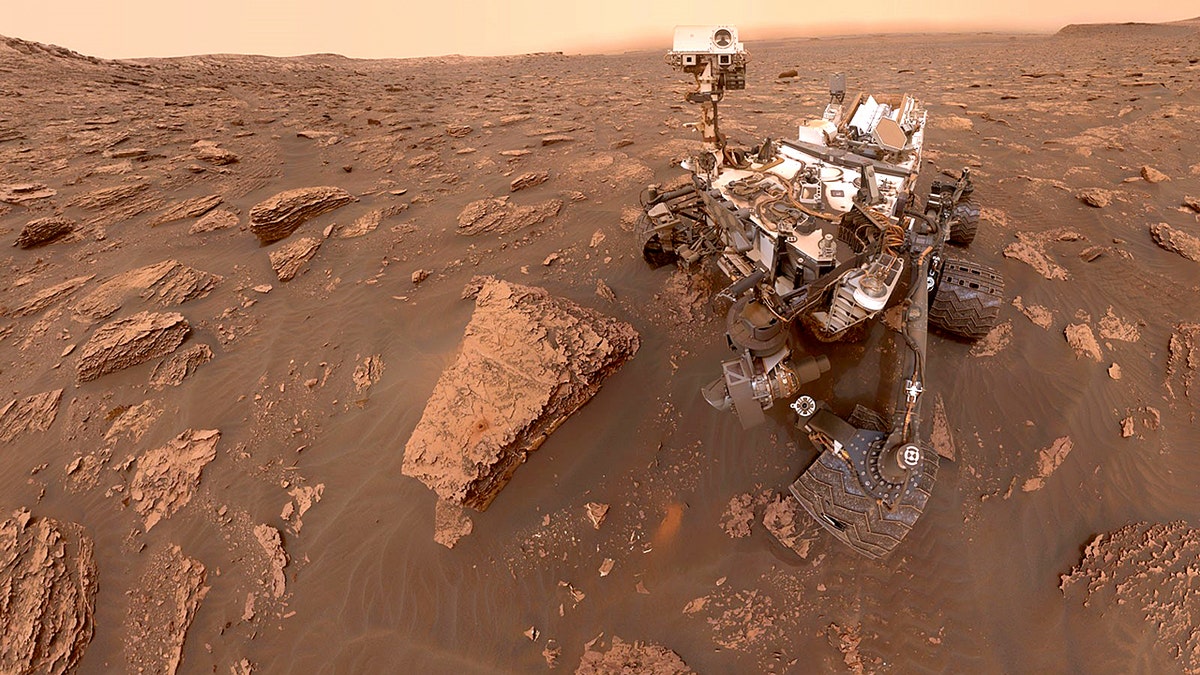
“The rover is currently exploring a layer with an abundance of salty minerals called magnesium sulfates, which form as water dries up,” NASA said. “Their presence here suggests this layer emerged as the climate became drier. “Remarkably, the boxwork patterns show that even in the midst of this drying, water was still present underground, creating changes seen today.”
Recent clues exposed on Mars may provide additional insight for scientists into why the boxwork patterns formed where they did.
The bedrock between the ridges has a lot of tiny fractures filled with white veins of calcium sulfate, which is a salty mineral left behind when groundwater trickles through cracks in rocks, NASA said. In the lower layers of the mountain, similar veins were plentiful, and one was even enriched with clays. But, until now, none of the veins had been spotted in the sulfate.
“That’s really surprising,” said Curiosity Deputy Project Scientist Abigail Fraeman of JPL. “These calcium sulfate veins used to be everywhere, but they more or less disappeared as we climbed higher up Mount Sharp. The team is excited to figure out why they’ve returned now.”
The Curiosity rover was launched Nov. 26, 2011, and landed on Mars Aug. 5, 2012. Its mission was to find out whether Mars ever had the right environmental conditions to support life, and, early on, the rover discovered chemical and mineral evidence of habitable environments from the past.
Read the full article here








